The human musculoskeletal system is a marvel of engineering, enabling us to perform a vast array of movements and tasks. One of the most intricate and versatile parts of this system is the arm. Comprising bones, muscles, tendons, and ligaments, the arm’s musculoskeletal structure allows for a wide range of movements, from delicate tasks like writing to powerful motions like throwing a ball.
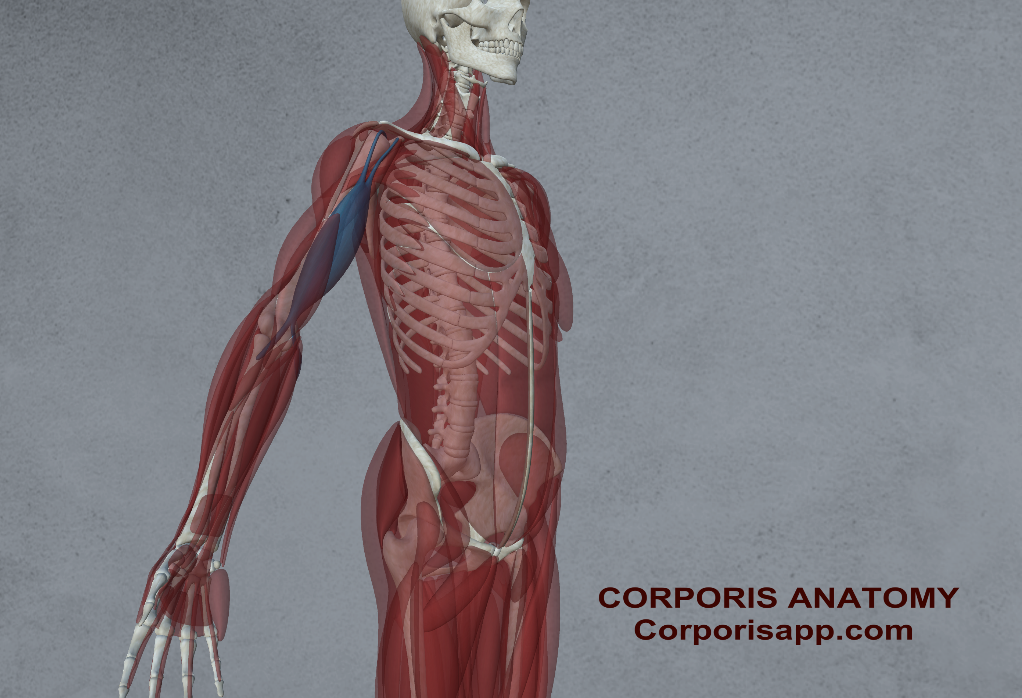
Bones of the Arm
The arm consists of three major bones: the humerus, radius, and ulna. The humerus is the long bone of the upper arm, connecting the shoulder to the elbow joint. It forms the primary support structure for the arm and provides attachment points for numerous muscles. The radius and ulna, located in the forearm, are parallel bones that allow for rotation of the forearm. The radius is on the thumb side of the forearm, while the ulna is on the pinky side.
Joints and Articulations
The arm is endowed with several joints that facilitate movement. The shoulder joint, also known as the glenohumeral joint, is a ball-and-socket joint formed by the articulation of the humerus with the scapula. This joint allows for a wide range of movements, including flexion, extension, abduction, adduction, and rotation.
The elbow joint, on the other hand, is a hinge joint formed by the articulation of the humerus with the ulna and radius. This joint primarily enables flexion and extension movements. The radius and ulna also articulate at the proximal and distal radioulnar joints, allowing for rotational movements of the forearm.
Muscles and Their Functions
A network of muscles envelops the bones of the arm, working in coordination to generate movement. These muscles can be broadly classified into flexors and extensors, each playing a crucial role in different types of movements.
Flexor Muscles
Biceps Brachii: This prominent muscle, located on the anterior side of the upper arm, is responsible for flexing the elbow joint. It is composed of two heads (long head and short head) that originate from different points on the scapula and merge to attach to the radius.
Brachialis: Found beneath the biceps brachii, the brachialis is the prime flexor of the elbow joint. It originates from the front of the humerus and attaches to the ulna.
Brachioradialis: Situated on the lateral side of the forearm, the brachioradialis assists in flexing the elbow. It originates from the distal end of the humerus and attaches to the radius.
Extensor Muscles
Triceps Brachii: Positioned on the posterior side of the upper arm, the triceps brachii is the primary extensor of the elbow joint. It comprises three heads (long head, lateral head, and medial head) that originate from different parts of the scapula and humerus, converging to attach to the ulna.
Tendons and Ligaments
Tendons are tough, fibrous connective tissues that connect muscles to bones. In the arm, tendons play a crucial role in transmitting the force generated by muscles to produce movement. For instance, the tendons of the biceps brachii, known as the biceps brachii tendons, attach to the radius, allowing the biceps to flex the elbow and supinate the forearm.
Ligaments, on the other hand, are strong bands of connective tissue that connect bones to other bones, providing stability to joints. In the arm, ligaments like the radial collateral ligament, ulnar collateral ligament, and annular ligament reinforce the stability of the elbow joint, preventing excessive lateral or medial movement.
Common Injuries and Care
Due to its extensive use in various activities, the arm is susceptible to injuries. These may range from minor strains and sprains to more serious conditions like fractures or dislocations. Proper warm-up, strength training, and ergonomic practices can help prevent many of these injuries. In case of an injury, seeking prompt medical attention and following a rehabilitation program is crucial for a full recovery.
Conclusions
The human arm is a remarkable example of the complexity and precision of the musculoskeletal system. Through the coordinated efforts of bones, muscles, tendons, and ligaments, it enables us to perform a diverse range of tasks essential for daily life. Understanding the intricacies of this system allows us to appreciate the intricacies of our own bodies and underscores the importance of caring for them.
In conclusion, the arm stands as a testament to the incredible capabilities of the human body and serves as a reminder of the importance of maintaining its health and functionality.
Do you want to test your knowledge? Try our quiz available in the quiz section!
